Content

Banks and other lenders won’t even consider loaning to a businesses on the cash method, especially if they have more than $500,000 in annual revenue. A bank will typically ask that you go back and hire an expert to provide more accurate (“legitimate”) financials using the accrual/GAAP method.
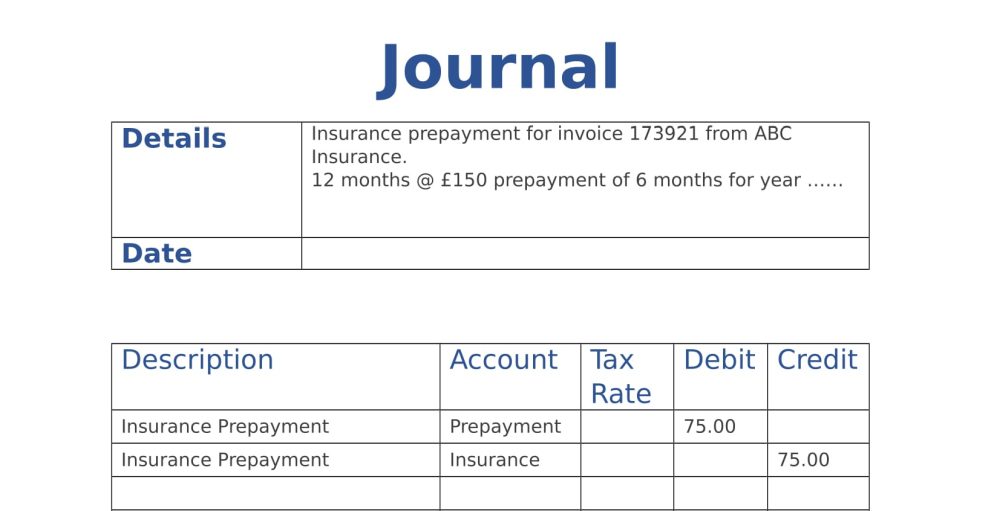
Under cash accounting, a business could avoid recording a loss for, say, the month of June simply by holding off on paying its bills until July 1. If September looks like it’s going to be a weak month for sales, a company could prop up the numbers by delaying the billing of some customers so that their payment doesn’t arrive until after Sept. 1.
Are You GAAP Ready? Tackling the Move from Cash to Accrual Accounting
Before 2017, small-business taxpayers with average annual gross receipts of $5 million or less in the preceding three-year period could use the cash method. The enactment of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act , however, made it possible for more small businesses to use the cash method. The TCJA allows small business taxpayers with average annual gross receipts of $25 million or less in the prior three-year period to use the cash method of accounting. If your business makes more than that, you must use the accrual method. While accrual accounting shows a more accurate picture of a company’s finances, it does have the potential to obscure short-term cash flow issues. This is because revenue reporting will include cash that is not yet usable to the business. The difference between accrual and cash based accounting is the time at which income and expenses are recorded.
Similarly, you only mark down expenses as that money leaves your account. That means cash basis accounting doesn’t take accounts payable and accounts receivable into account. The real difference between accrual basis accounting and cash basis is the timing of revenues and expenses, meaning that the time period for which we are reporting becomes extremely relevant. Imagine if Ford Motor Company, which was found back on June 16, 1903, tried to create an income statement for the whole time it had been in business. Not only would the income statement be kind of a mess, but it also wouldn’t really be relevant for current decision making. GAAP recognizes the cash accounting method as an unembellished and accurate basis of accounting.
Cash accounting vs accrual accounting
When GAAP is followed, companies prepare financial statements using the accrual method of accounting. If cash transactions are paid when goods are received, or cash is received when the product is delivered, there are no differences between cash basis and accrual basis accounting methods. For example, a company should record an expense for estimated Why Does GAAP Require Accrual Basis Accounting? bad debts that have not yet been incurred. By doing so, all expenses related to a revenue transaction are recorded at the same time as the revenue, which results in an income statement that fully reflects the results of operations. Similarly, the estimated amounts of product returns, sales allowances, and obsolete inventory may be recorded.
Pitney Bowes Announces Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 … – businesswire.com
Pitney Bowes Announces Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 ….
Posted: Tue, 31 Jan 2023 12:00:00 GMT [source]
When utilities or rent are billed after the period to which they apply, the company accrues the expense during the period that it uses the utilities or rented property. To record cash received and eliminate the amount owed by Smith’s Computers.
Cash vs. Accrual Accounting: The Bottom Line
However, if you do some transactions on credit, as in most business, the results will vary. We record revenue as it is earned and we also record a receivable, which is basically and IOU from the customer to us. Later, when the cash is received, we eliminate the receivable, which is an asset to us because we own it and it is worth money, and we show a deposit in our bank account. Similarly, revenue https://online-accounting.net/ is realizable when there is good reason to believe it will be collected, and that is the test for accruing revenue. In other words, in order for revenue to be recognized, it must be realizable—it must be fairly certain that the company will collect it. In accounts receivable , whether you use accrual or cash basis accounting will determine when you recognize revenue after making a sale on credit.
What is the difference between GAAP and accrual?
Unlike cash and accrual, GAAP is not a form of accounting but a set of widely accepted standards and rules set in place to ensure companies account for their financials in the same way. Accrual is the acceptable form of accounting under GAAP's rules. Cash is not.
For instance, consider a software company that sells a five-year subscription to its solution and receives the full payment as a cash sum at the start of the subscription. With cash-based accounting, it would record all the revenue during the first period and nothing for the next five years, which could lead to vastly different numbers in two consecutive reporting periods. With accrual-based accounting, the company spreads out that revenue over the length of the subscription to smooth out the impact of that transaction. Accrual accounting generally makes the relationships between revenue and expenses clearer, providing better insight into profitability. It also offers a more accurate picture of a company’s assets and liabilities on its balance sheet. For these reasons, accrual basis accounting is the only method allowed under General Accepted Accounting Principles and is required by the Securities and Exchange Commission for publicly traded companies. With cash-based accounting, you only record revenue when you’ve actually received the money.
Best Podcasts for Small Business Owners and CEO’s
But, with the transition from cash to accrual accounting, the workforce can be held accountable for their actions. So when you sell goods and services, you don’t enter them into the books until you receive the payment against them.
- Providing a correct representation of the company’s financial health is especially important for larger companies that report to external stakeholders like their board of directors.
- While a sole proprietorship can get away with using the cash based accounting method, as your business grows it may be time to make the jump to accrual concepts.
- Since the IRS requires most nonprofit organizations to file a 990 information return, accrual basis accounting is preferable because it allows for GAAP compliance.
- Accrual accounting recognizes costs and expenses when they occur rather than when actual cash is exchanged.
At times, it makes sense for businesses to use both cash and accrual accounting. The bonus is paid in 2018 based on 2017 results of operations as shown on the audited financial statements. Under GAAP, the bonus would be recorded and shown as an expense in 2017, matching it against 2017 sales revenue. The Accounting Rate of Return is a capital budgeting metric for long-term investments.
What Is Cash Accounting?
Specifically, companies have to factor in accounts payable and accounts receivable . That means you’re accounting for money that hasn’t technically changed hands yet. Let’s say that a company pays for items of property, plant, and equipment in cash, it will record a reduction in cash and an increase in long-term assets, and no expense is recorded.
What are the three major reasons for accrual accounting?
- Improving Your Financial Picture.
- Staying GAAP Compliant.
- Improving Accuracy.
- Planning for Growth.
- Obtaining Credit.
Cash accounting doesn’t give the clear picture of financial performance that’s needed for key stakeholders like tax authorities, regulators, and investors. For these reasons, small businesses and solo entrepreneurs tend to favor cash accounting.
